- Home
- Blog
- Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
- Hearing Loss: Causes, Types, and Preventions

Hearing Loss: Causes, Types, and Preventions
Employee safety must always be the top priority in the workplace. When the risk of occupational hazards increases in certain professions, preventative measures to protect employees become increasingly crucial. The risks increase significantly when employees are exposed to consistent loud noise as part of their daily roles. A deep understanding of the causes, effects and prevention measures available can help to protect employees at risk.
Loud Noises: One of the Leading Causes of Hearing Loss
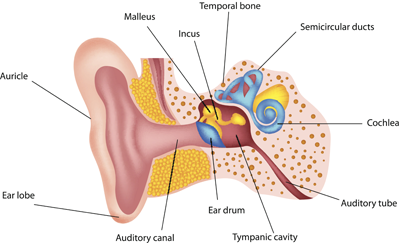
Loud noises commonly cause hearing loss over time. Specifically, the inner compartments of the ear easily become damaged when the ear is exposed to repeated, regular loud noises over a long period of time. Whereas age-related hearing loss happens naturally and gradually over time, noise-induced hearing loss occurs with regular exposure to loud noises. This exposure speeds up the process of natural hearing loss over time.
Noise-induced hearing loss occurs due to damage to the cochlea. The cochlea is a coiled, spiral tube section in the inner ear where sensitive hair cells become tarnished. While there are varying degrees of hearing loss (do you know how to recognize the 7 degrees of hearing loss?), there are three main types of hearing loss. According to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA), these three basic types are conductive hearing loss, sensorineural hearing loss, and mixed hearing loss.
Types of Hearing Loss
1. Conductive Hearing LossConductive hearing loss occurs when sound cannot make it through the outer and middle ear to reach the inner ear. With this type of hearing loss, it becomes harder to hear soft sounds and louder sounds may be muffled. Oftentimes, medication or surgery can fix conductive hearing loss.
Conductive hearing loss can be caused by the following:
- Fluid in the middle ear caused by colds/allergies
- Ear infection
- Poor Eustachian tube (connects the middle ear to noise) function
- Hole in eardrum
- Benign tumors
- Earwax stuck in the ear canal
- Swimmer’s ear infection
- Object stuck in the outer ear
- Deformation of the outer or middle ear
Sensorineural hearing loss is caused by inner ear damage, such as problems with the nerve pathways from the inner ear to the brain. This is the most common type of hearing loss and is oftentimes permanent. However, hearing aids may help with this type of degradation. With this hearing loss, soft sounds may be hard to hear, and loud sounds may be unclear or muffled.
This type of hearing loss can occur when working in loud or extreme noise environments. Tinnitus (ringing in the ears or hearing different disruptive sounds such as hissing, buzzing, whistling, or humming) can be a symptom of this type of hearing loss.
Sensorineural hearing loss can be caused by the following:
- Illnesses
- Drugs that are toxic to hearing
- Genetic hearing loss
- Aging
- Blow to the head
- Deformation in the inner ear
- Loud noises or explosions
Mixed hearing loss happens when conductive hearing loss and sensorineural hearing loss occur at the same time. This means that there is damage in the outer or middle ear and in the inner ear. This happens when working in loud-noise environments. Together, conductive hearing loss and sensorineural hearing loss can make hearing worse than with only one problem.
Preventing Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in the Workplace
To decrease the risk of hearing loss in such circumstances, individuals need to get in the habit of using the right kind of ear protection. Protective earplugs and headsets can make an important difference in protecting the ear health of employees. Most protective equipment does not work effectively for hearing-impaired individuals using hearing aids and can cause more harm than good if they remove these devices in high-noise environments. This is not the case with Sensear’s smart communication headsets, as our headsets pair well with hearing aids.
Sensear’s SENS® Technology in our Digital Communication Headsets suppresses noise in the surrounding environment while allowing users to still communicate with each other. The innovative SENS® Technology works by limiting loud background noises while processing and separating speech, allowing the wearer to hear speech, alarms, or other important sounds. This is perfect for potentially dangerous environments such as factories, heavy industrial sites, etc. where workers need to be able to hear their coworkers yet require loud machinery noises to be suppressed.
Use our Hearing Protection Calculator to calculate the sound level at the ear when wearing hearing protection. If your HPDs are not providing the correct level of hearing protection for your workers, choose the right hearing protection and prevent hearing loss. Contact us today for a free consultation to discuss your concerns or download our Buyer’s Guide to Communication Headsets.









